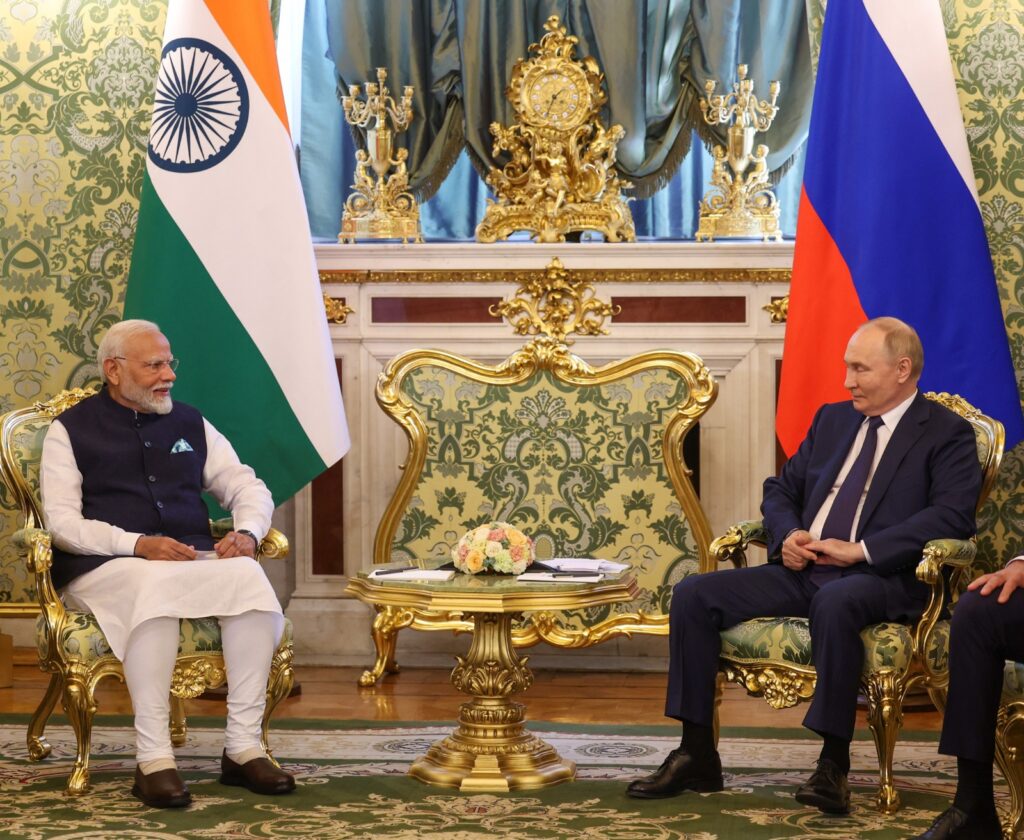
Prime Minister of the Republic of India Shri Narendra Modi paid an official visit to the Russian Federation on July 8-9, 2024 at the invitation of President of the Russian Federation H.E. Mr. Vladimir Putin for the 22nd India – Russia Annual Summit.
2. During the visit, H.E. Mr. President Vladimir Putin conferred Russia’s highest civilian honour the “Order of Saint Andrew the Apostle” on Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi for his distinguished contribution to the development of Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership between India and Russia and friendly ties between the peoples of the two countries.
Political relations
3. The Leaders noted the continued strengthening and deepening of the Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership between India and Russia.
4. The Leaders highly appreciated the special nature of this time-tested relationship which is based on trust, mutual understanding and strategic convergence. Regular bilateral engagement at all levels, including during India’s Chairship of SCO and G20 in 2023 and under Russia’s Chairship of BRICS in 2024, helped in further deepening and expansion of the growing bilateral partnership.
5. The Leaders positively assessed the multi-faceted mutually beneficial India-Russia relations that span all possible areas of cooperation including political and strategic, military and security, trade and investment, energy, science and technology, nuclear, space, cultural, education and humanitarian cooperation. It was noted with satisfaction that both Sides are actively exploring new avenues for cooperation while further strengthening cooperation in the traditional areas.
6. The Sides underlined that India-Russia ties have remained resilient in the backdrop of the prevailing complex, challenging and uncertain geopolitical situation. Both Sides have strived to forge a contemporary, balanced, mutually beneficial, sustainable and long-term partnership. Development of the India-Russia relations over the entire spectrum of cooperation areas is a shared foreign policy priority. The Leaders agreed to make all efforts to unlock the full potential of the strategic partnership.
Cooperation at the level of Foreign Ministries
7. The Leaders appreciated the close cooperation between the Foreign Ministries and frequent meetings and exchanges between the Foreign Ministers for nurturing and steering the bilateral partnership through the constantly evolving and complex geopolitical scenario and adapting it to the changing circumstances. The regular close engagement has also helped in a deeper understanding and appreciation of each other’s core interests, positions on international issues and in various international and multilateral organizations.
8. The Leaders welcomed the Protocol on Foreign Office Consultations for the period 2024-28 signed in December 2023 between the Ministry of External Affairs of India and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation which lays down the foundation for exchanges and dialogue on most pressing bilateral, global and regional issues. They noted with satisfaction the regular holding of Foreign Office Consultations on bilateral, UN related, Counter-Terrorism, Consular and Property matters as well as regional and global issues of mutual interest.
Parliamentary Cooperation
9. The Sides noted the close inter-parliamentary interaction and underlined the importance of regular meetings of Inter-Parliamentary Commission and Parliamentary Friendship Groups of both Houses as a valuable component of India-Russia relations. They appreciated the visit of the Speaker of the Russian Federation Council to New Delhi in October 2023 for the 9th G20 Parliamentary Speakers’ Summit.
Cooperation between National Security Councils
10. The Leaders highlighted the importance of the security dialogue at the level of National Security Advisors and the National Security Councils on bilateral and regional issues and welcomed regular interactions which facilitated greater strategic understanding and coordination between the two countries on bilateral as well as global and regional issues of mutual concern.
Trade and Economic partnership
11. The Sides noted with satisfaction the significant growth of bilateral trade in 2023 which is around double of the bilateral trade target of USD 30 billion set by the Leaders for 2025. To achieve balanced and sustainable bilateral trade in long term, the Leaders stressed the need to increase Indian exports to Russia through strengthening industrial cooperation, forging new technological and investment partnerships, especially in advanced high-technology areas and finding new avenues and forms of cooperation.
12. Aiming to further accelerate and sustain the growth in bilateral trade, the Leaders agreed to set the bilateral trade target of USD 100 billion by 2030.
13. The Leaders welcomed the 24th Session of the India-Russia Intergovernmental Commission on Trade, Economic, Scientific, Technical and Cultural Cooperation (IRIGC-TEC) and India-Russia Business Forum held in New Delhi in April 2023, and the inaugural meetings of the Working-Groups and Sub-Working Groups on Transport, Urban Development and Railways. They appreciated the work of the Commission for ensuring further expansion and diversification of bilateral economic relations. They agreed to hold the next session of IRIGC-TEC in the second half of 2024 in Russia.
14. The Leaders, seeking to provide an additional impetus to the deepening of the trade and economic cooperation and guided by the intention to maintain the trend of dynamic growth in trade of goods and services between the two states and the desire to ensure a significant increase in its volume, instructed the concerned agencies to prepare a Programme for the development of promising areas of Russian-Indian economic cooperation till 2030 (Programme-2030). The Sides reaffirmed readiness to contribute
to the implementation of the initiatives, projects, measures and activities provided for by the Programme-2030. The overall coordination of its implementation will carried out by the IRIGC-TEC. Its Working Groups and Sub-Working groups, as well as concerned agencies of the two countries are instructed to ensure monitoring, control and support of the Programme-2030.
15. The Sides agreed to continue working together to promote bilateral settlement system using national currencies. The Sides agreed to continue consultations for interoperability of their financial messaging systems. They noted the importance of finding mutually acceptable solutions for issues of insurance and reinsurance for facilitating further enhancement in bilateral trade.
16. For eliminating the non-tariff/tariff barriers in trade, including protective measures and administrative barriers, the Leaders appreciated the initial meeting in March 2024 to commence full negotiations for a Free Trade Agreement on goods between India and the Eurasian Economic Union. The Leaders also directed their relevant officials to explore the possibility of commencing negotiations for signing a bilateral free-trade agreement in services and investments.
17. Noting the great significance of industrial cooperation for the development of bilateral relations, the Sides confirmed their mutual aspiration for the strengthening of manufacturing cooperation in the fields of transport engineering, metallurgy, chemical industry and other sectors of mutual interest. The Sides expressed their intention to create favorable conditions for the implementation of promising joint projects in priority areas. The Sides emphasized the importance of expanding reciprocal trade flows of industrial products and increasing their share in bilateral trade.
18. The Sides reaffirmed that the Agreement between the Federal Customs Service of Russia and the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs of India on mutual recognition of the relevant institutions of the Authorized Economic Operator, signed in May 2024, will provide an additional impetus to the expansion of the nomenclature and increase the volume of Russia-India trade, as well as ensure the security of supply chains.
19. The Sides agreed to continue discussion on the Migration and Mobility Partnership Agreement between the Government of the Russian Federation and the Government of the Republic of India.
20. The Sides agreed to continue cooperation on the sustainable supply of fertilizers to India on the basis of company to company long-term contracts within the framework of Joint India-Russia Committee on Fertilizers.
21. The Leaders welcomed the first ever India-Russia Investment Forum and
the 7th meeting of Working Group on Priority Investment Projects in April 2024 in Moscow where the Sides agreed to facilitate participation of Russian businesses in “Make in India” and “Atmanirbhar Bharat” Programmes and that of Indian companies in investment projects in Russia. The Indian Side invited Russian businesses to set up manufacturing facilities in greenfield industrial cities under Industrial Corridor program of Government of India.
22. The Sides confirmed their interest in expanding cooperation in the field of communication technologies, including telecommunications, satellite communications, digitalization of public administration and the urban environment, mobile communications, information security, etc.
Transport and Connectivity
23. The Sides share approaches on building a new architecture of stable and efficient transport corridors, and pay close attention to the development of promising production and marketing chains in Eurasia, including for the purpose of implementing the idea of a Greater Eurasian space. In this context, the Sides expressed readiness to actively work to expand logistics links with an emphasis on increasing the capacity of infrastructure, including for implementation of the Chennai-Vladivostok (Eastern Maritime) Corridor and the International North-South Transport Corridor, as well as using the potential of the Northern Sea Route.
24. Both Sides will continue joint efforts to intensify the use of INSTC route in order to reduce the time and cost of cargo transportation and to promote connectivity in the Eurasian space. Cooperation in the field of transport and logistics will be based on the principles of transparency, broad participation, local priorities, financial sustainability and respect for sovereignty and territorial integrity of all nations.
25. The Sides support cooperation in developing shipping between Russia and India via the Northern Sea Route. For this purpose, they expressed readiness to establish a joint working body within the IRIGC-TEC for cooperation on the Northern Sea Route.
26. The Sides noted with satisfaction the results of the meeting of the Sub-Working Group on Civil Aviation (February, 2023) in Moscow. They agreed to continue cooperation in the field of civil aviation and civil aviation security.
Energy partnership
27. The Sides reiterated the importance of the robust and wide ranging cooperation in the energy sector as a significant pillar of the Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership. In this context, the Sides noted the continued special importance of bilateral trade in energy resources and agreed to explore new long term contracts.
28. The Sides appreciated the ongoing cooperation in the coal sector and agreed to explore the possibility for further increasing supply of coking coal to India, and the opportunities of exporting anthracite coal from Russia to India.
Cooperation in the Russian Far East and Arctic
29. The Sides their readiness to intensify trade and investment cooperation in the Far East and the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation. In this regard, the Sides welcomed the signing of the Program of India-Russia cooperation in trade, economic and investment spheres in the Russian Far East for the period from 2024 -2029, as well as of cooperation principles in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation. The Program of Cooperation will provide the necessary framework for further cooperation between India and the Russian Far East region, especially in the sectors of agriculture, energy, mining, manpower, diamonds, pharmaceuticals, maritime transport, etc.
30. The Sides reiterated the need for the development of interregional dialogue between the regions of the Russian Far East and the Indian States and encourage the establishment of twinning relations to develop business, trade, educational, cultural exchanges and projects.
31. The Russian side invites interested Indian investors to implement high-tech investment projects within the framework of the Territories of Advanced Development in the Russian Far East. The Indian Side appreciated participation of the delegation of the Russian Ministry of Far East and Arctic Development in the Vibrant Gujarat Global Summit in January 2024. The Russian Side welcomed the participation of Indian delegations in the Saint Petersburg International Economic Forum (June 2023) and the Eastern Economic Forum (September 2023). The Sides noted the contribution of India-Russia Business Dialogue organized on the sidelines of these economic forums for promotion of bilateral trade, economic and investment cooperation.
32. The Sides recognize the importance of developing cooperation at leading business arenas in the Asia-Pacific region, including within the framework of the Eastern Economic Forum.
Civil Nuclear Cooperation, Cooperation in Space
33. The Sides noted the importance of the cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy as a significant component of the strategic partnership. The Sides welcomed the progress achieved in the construction of the remaining nuclear power plant units at Kudankulam and agreed on adhering to the schedule, including to the timelines for delivery of supplies. Both Sides noted the importance of further discussion on the second site in India in accordance with earlier signed agreements. The Sides agreed to continue technical discussions on the VVER 1200 of the Russian design, localization of equipment and joint manufacturing of NPP components as well as on cooperation in third countries. The Sides confirmed their intention to broaden cooperation in Nuclear Power including fuel cycle, life cycle support for operating KKNPPs and non-power applications.
34. Noting the importance of cooperation in Space, the Sides welcomed the enhanced partnership between the Indian Space Research Organization and the Russian State Space Corporation “Roscosmos” in the use of outer space for peaceful purposes, including in the human spaceflight programs, satellite navigation and planetary exploration. The Russian Side congratulated India on successful landing of Chandrayaan-3 as a long stride in the exploration of outer space and the impressive progress made by India in science and engineering, which can be mutually beneficial for future cooperation. The Sides agreed to explore prospects of mutually beneficial cooperation in rocket engine development, production and use.
Military and Military Technical Cooperation
35. Military and Military-Technical Cooperation has traditionally been the pillar of Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership between India and Russia, which has grown from strength to strength through several decades of joint efforts and fruitful cooperation, steered by the Intergovernmental Commission on Military and Military Technical Cooperation (IRIGC-M&MTC).The Sides expressed their satisfaction with regular defence and military contacts, including the meeting of Defence Ministers in New Delhi in April 2023 on the sidelines of the SCO Defence Ministers’ Meeting and joint exercises of the Armed Forces of the two countries. They agreed to hold the 21st round of IRIGC-M&MTC in Moscow in the second half of 2024. Responding to India’s quest for self-sufficiency, the partnership is reorienting presently to joint research and development, co-development and joint production of advanced defence technology and systems. The Sides confirmed commitment to maintain the momentum of joint military cooperation activities and expand military delegation exchanges.
36. Both Sides agreed to encourage joint manufacturing in India of spare parts, components, aggregates and other products for maintenance of Russian origin arms and defence equipment under Make-in-India program through transfer of technology and setting up of joint ventures for meeting the needs of the Indian Armed Forces as well as subsequent export to mutually friendly third countries by the Sides’ approval. In this regard, the Sides agreed on establishing a new Working Group on Technological Cooperation and discussing its provisions during the next meeting of IRIGC-M&MTC.
Cooperation in Education and Science & Technology
37. The Sides noted the importance of bilateral cooperation in science, technology and innovation, confirmed mutual interest in developing partnerships between educational and scientific organizations, including the implementation of various academic mobility forms, educational programs and research projects, as well as cooperation in the opening of branches of interested Russian educational and scientific organizations in India.
38. The Sides noted the successful implementation of the Roadmap between the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation and the Department of Science and Technology of the Government of the Republic of India, 2021, including the implementation of Russia-India research projects through ministries and scientific foundations of the two countries.
39. Emphasizing the importance of joint research in science, technology and innovation, the two Sides agreed to work together in the framework of the Roadmap for Science, Technology & Innovation Cooperation of 2021 to boost innovation-related collaborations between the two countries, and focus on commercialization of technologies and full-cycle support to joint projects for economic and societal impact. Both sides agreed to explore the creation of International centers for Innovative Entrepreneurship & Inter-Cluster Interactions to improve Technology Partnerships.
40. The Sides identified potential areas of cooperation as agriculture and food science and technology, ship building and repair, blue economy, marine industry & ocean resources, chemical science & technology, energy, water, climate, and natural resources, health and medical technology, life sciences, and biotechnology, applied mathematics and data science and technology, material science & technology, physics and astrophysics, polar research and nanotechnology.
41. The Sides also noted the successful implementation of joint bids for joint research projects by the Department of Science & Technology, Government of India, and the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation, as well as with the Russian Science Foundation in areas of mutual interest.
42. The Sides reiterated their intention to establish a Working Group on higher education within the framework of the IRIGC-TEC, involving representatives of interested departments and organizations of two countries to address topical issues of interaction
in this field.
43. The Sides agreed to continue their consultations on mutual recognition of education and academic degrees.
44. The Sides expressed support for holding of Russia-India round tables, seminars, conferences and other activities aimed at enhancing and expanding bilateral educational and scientific ties.
45. Recognizing the traditionally strong cooperation between India and Russia in the sphere of education, the Sides agreed to continue their efforts in promoting linkages between universities and educational institutions and in this regard welcomed the Education Summit organised in India with participation of about 60 Russian universities in April 2024.
Cultural cooperation, Tourism and people to people exchanges
46. The Sides agreed that cultural interaction is an important component of the Russia-India Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership. The Sides support and encourage the establishment of direct contacts and further cooperation between ensembles, theaters, libraries, museums, creative universities and other cultural institutions of the two countries.
47. Underlining the traditionally robust cultural linkages, the Sides appreciated
the successful implementation of Cultural Exchange Programme between the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Culture of the Government of the Republic of India for 2021-2024, which plays a crucial role in enhancing people to people contacts. It was agreed to continue the mutually beneficial practice of reciprocally holding cultural and film festivals. The need for geographical expansion of cultural exchanges and greater involvement of the youth and folk art groups was also highlighted. In this regard, the Sides noted with satisfaction the successful holding of Festival of Indian Culture in eight cities of Russia in September 2023, and welcomed the Festival of Russian Culture in India in 2024.
48. Noting the important role of youth in promoting the bilateral relations the Leaders noted with satisfaction the enhanced youth exchanges through the active participation of Indian delegation of students and young entrepreneurs in the Sochi World Youth Festival in March 2024 and Indian sportspersons and athletes in the “Games of the Future” and BRICS Games in Kazan in March and June 2024 respectively.
49. The Sides also emphasized the need to promote a more contemporary understanding of both countries in addition to the cultural exchanges which may include large scale exhibitions and exchanges in areas like science and technology, green energy, space etc. In this regard the Sides agreed to hold “Cross/Multi-Sectoral Years of Exchange” in both countries for enhanced people to people exchanges and bringing together the economic, educational, scientific and civil societies.
50. The Sides agreed to continue their joint efforts in promoting Russian language in India and Indian languages in Russia comprehensively, including by developing contacts between relevant educational institutions.
51. The Sides noted with appreciation the enhanced exchanges and contacts between the experts, think-tanks and institutes of India and Russia. Over the years, this track of dialogue has promoted increased mutual understanding between Indian and Russian strategic and policy making circles and businesses so as to further strengthen the Strategic Partnership.
52. The Sides appreciated the steady increase in tourist exchanges between Russia and India. To further deepen the cooperation in tourism, the Sides agreed to cooperate both at government and private sector level with the aim to enhance tourist flows. In this context, the Sides noted the participation of Indian tour operators, tourism Departments of Indian states under the leadership of Incredible India team in popular Russian tour exhibitions like Moscow International Tourism and Travel Expo 2023 & 2024 and OTDYKH-2023.
53. The Sides welcomed simplification of visa formalities, including introduction of e-Visa by both countries. They agreed to continue the work on further simplification of the visa regime in future.
Cooperation in the UN and multilateral fora.
54. The Sides noted the high level of political dialogue and cooperation between two countries on issues at the UN and agreed to deepen it further. Both Sides stressed the importance of reinvigorating multilateralism, with the central coordinating role played by the United Nations in world affairs. The Sides underlined the primacy of respect for international law and emphasized their commitment to the purposes and the principles stated in the UN Charter including the principle of non-interference in the internal affairs of Member States.
55. Russia appreciated India’s 2021-22 term as non-permanent member of the UN Security Council and India’s UNSC priorities and efforts towards reformed multilateralism, UN peacekeeping and counter-terrorism. Both Sides highlighted that India’s presence in the UNSC provides a valuable opportunity to further coordinate on most pressing issues at the UN.
56. Both Sides called for comprehensive reform of the UNSC to reflect contemporary global realities and to make it more representative, effective and efficient in dealing with issues of international peace and security. Russia reiterated its steadfast support for India’s permanent membership of a reformed and expanded UN Security Council.
57. The Sides highlighted their fruitful cooperation within the G20 format especially under India’s Presidency of the G20 in 2023 under the theme “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” or “One Earth One Family One Future” which also put forth Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi’s initiative of Lifestyles for Sustainable Development (LiFE) to combat Climate Change. President H.E. Mr. Vladimir Putin highly appreciated the success of Indian Presidency of G20 under the leadership of Prime Minister Modi which emphasized just and equitable growth for all, human-centric approach while supporting innovation and digital technology, including Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) as a critical enabler for inclusive development, and renewed faith in multilateralism. The Indian side appreciated Russia’s consistent support for India’s successful G20 Presidency.
58. The Sides emphasized that the important practical legacy of India’s G20 Presidency was the consolidation of the priorities of the countries of the Global South in the agenda of the main platform for international economic and financial cooperation, as well as the entry of the African Union into the ranks of full members of the forum. The Sides also welcomed the holding of the Voice of Global South virtual summits under the auspices of the Indian Presidency in 2023, which sent an important signal in favor of building a multipolar world order and strengthening the position of developing countries in global affairs. They agreed to continue to strengthen coordination within the G20 in order to develop joint solutions to global economic challenges, mobilize increased access to climate finance and technology as envisaged in the Green Development Pact enshrined in the New Delhi G20 Leaders’ Declaration, and ensure just reform of international economic governance institutions, especially the Multilateral Development Banks.
59. The Sides stressed the importance of strengthening their strategic partnership and close coordination within BRICS, and welcomed the decision to expand the membership of BRICS that was taken at the XV summit in Johannesburg. They reaffirmed their commitment to the BRICS spirit featuring mutual respect and understanding, equality, solidarity, openness, inclusiveness, and consensus. Russia and India agreed to continue joint efforts aimed at ensuring continuity and consolidation of BRICS cooperation, seamless integration of new members in BRICS, and developing modalities for establishing a BRICS Partner Country Model. The Russian Side expressed gratitude to India for supporting the priorities of the Russia’s Chairship in 2024.
60. The Sides welcomed the new member States to the expanded BRICS family. India expressed its full support to Russia’s BRICS Chairship in 2024 under the theme “Strengthening Multilateralism for Just Global Development and Security”. The Sides expressed their commitment to working together for the success of the XVI BRICS Summit in October 2024 in Kazan.
61. The Sides consider joint work within the framework of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization to be important for deepening the relations of Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership between Russia and India.
62. The Sides noted with satisfaction their fruitful cooperation within SCO on key areas like countering terrorism, extremism, separatism, drug trafficking, cross-border organized crime, and information security threats. Russia appreciated India’s SCO Chairship of 2022-23 and acknowledged that it added new momentum to the wide areas of cooperation in SCO. They welcomed the increased role of SCO in international affairs and in the formation of a sustainable and multipolar world order. They welcomed Iran and Belarus as new members of SCO. The Sides support the enhancement of the role of the SCO on the international arena, the comprehensive development of the organization’s contacts with the UN and its specialized agencies, as well as with other multilateral organizations and associations.
Counter terrorism
63. The Leaders unequivocally condemned terrorism and violent extremism conducive to terrorism in all its forms and manifestations including the cross-border movement of terrorists, and terrorism financing networks and safe havens. They strongly condemned the recent dastardly terrorist attack on an Army convoy in Kathua area of Jammu & Kashmir on 8th July 2024, in Dagestan on 23rd June and on the Crocus City Hall in Moscow on 22nd March and stressed that these terrorist attacks are a grim reminder for further strengthening cooperation to combat terrorism. The Sides called for an uncompromising fight against international terrorism and extremism in all their forms and manifestations, noting the importance of increasing cooperation in this area, without hidden agendas and double standards on the solid basis of international law and the UN Charter. Besides, they stressed the need for firm implementation of relevant resolutions of the UN Security Council, the UN General Assembly, as well as the implementation of the UN Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy.
64. The Sides emphasized the primary responsibility of States and their competent authorities in combating terrorism and that global efforts to prevent and counter terrorist threats must fully comply with their obligations under international law. They called for zero tolerance for terrorism and expeditious finalization and adoption of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism in the UN framework as well as implementation of the UNGA and the UNSC resolutions on countering terrorism and violent extremism, conducive to terrorism.
65. The Leaders reiterated that terrorism should not be associated with any religion, nationality, civilization or ethnic group and that all those involved in terrorist activities and their supporters must be held accountable and brought to justice in accordance with international law.
66. The Sides highly appreciated the Special Meeting of the UNSC Counter Terrorism Committee (CTC) held in India in October 2022 under India’s Chairship of the CTC and welcomed the unanimously adopted Delhi Declaration on countering the use of new and emerging technologies for terrorist purposes. They noted that the declaration aims to cover the main concerns surrounding the terrorist exploitation of Information and Communications Technology, such as payment technologies, social media platforms and fundraising methods and misuse of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV, or drones).
67. The Sides reaffirmed their commitment to strengthening multilateral cooperation in the field of combating transnational organized crime, countering money laundering, terrorist financing and drug trafficking.
68. The Sides expressed their readiness to strengthen the dialogue in the field of security in the use of ICTs on the basis of the Agreement on Cooperation in International Information Security dated October 15, 2016. Both Sides stressed the importance of strict compliance with the principles of sovereign equality of States and non-interference in their internal affairs. Towards this end both Sides urged to adopt universal international legal instruments and welcome efforts under the aegis of the United Nations, including the comprehensive convention on combating ICT crime.
69. The Sides intend to strengthen cooperation within the UN Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (UN COPUOS), including the issues of the long-term sustainability of outer space activities.
70. The Sides reaffirmed their commitment to further strengthening global efforts for non-proliferation of weapons of mass destruction. Russia expressed its strong support for India’s membership of the Nuclear Suppliers Group. The Sides urged all members of the international community to work towards enhancing the level of mutual trust, in order to promote global peace and security.
71. The Indian Side looked forward to Russia’s joining of the International Solar Alliance (ISA), the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) and the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA).
72. The Sides noted with appreciation the close coordination between India and Russia on Afghanistan including through the dialogue mechanism between the Security Councils of both countries. Both Sides discussed the situation in Afghanistan, including the security situation and its implications in the region, the current political situation, issues related to terrorism, radicalization and drug trafficking. They advocated for Afghanistan as an independent, united and peaceful state free from terrorism, war and drugs, living in peace with its neighbors and ensuring respect for basic human rights and freedoms, including for the most vulnerable sections of the Afghan society. They emphasized the important role of the Moscow Format meetings to facilitate the Afghan settlement.
73. The Leaders welcomed the counter-terrorism measures against international terrorist groups, including in particular ISIS, and other groups and expressed confidence that the fight against terrorism in Afghanistan would be comprehensive and effective. They stressed the need to ensure urgent and uninterrupted humanitarian assistance to the Afghan people without any political demands.
74. The Sides highlighted the imperative of peaceful resolution of the conflict around Ukraine through dialogue and diplomacy including engagement between both parties. They noted with appreciation relevant proposals of mediation and good offices aimed at peaceful resolution of the conflict in accordance with international law and on the basis of the UN Charter.
75. The Sides expressed deep concern on the situation in the Middle East, with a particular focus on Gaza. In this regard they called for the effective implementation of the relevant UNGA resolutions and UNSC resolution 2720 and for immediate safe and unhindered delivery of humanitarian assistance at scale directly to the Palestinian civilian population throughout the Gaza Strip. They also called for the effective implementation of the UNSC resolution 2728 for a lasting and sustainable ceasefire. They equally called for
the immediate and unconditional release of all hostages as well as humanitarian access to address their medical and other humanitarian needs. They reaffirmed their support for Palestine’s full membership in the United Nations and reiterated their unwavering commitment to the principle of the two-state solution according to internationally accepted basis.
76. The Sides agreed to strengthen joint efforts to build an architecture of equal and indivisible regional security and to intensify consultations on complementarities between integration and development initiatives in Greater Eurasian space and in the regions of Indian and Pacific oceans.
77. The Sides underlined the importance of strengthening cooperation within various regional fora, aimed at deepening regional peace and security, including East Asia Summit, ASEAN Regional Forum on Security (ARF), ASEAN Defence Ministers Meeting Plus (ADMM-Plus).
78. The Sides noted the importance of expanding efforts to combat climate change and achieving the goals of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Paris Agreement. In this regard the Sides agreed to develop cooperation in the field of preventing climate change and adapting to it, including the exchange of experience on the organization and operation of greenhouse gas emission quota systems, the implementation of joint Russian-Indian investment projects in the field of low-carbon development, as well as sustainable and “green” financing.
79. The Sides agreed to continue interaction within G20, BRICS, SCO on key issues such as increasing the sustainability and developing resiliency of international supply chains, compliance with free and fair trade rules and climate change. They welcomed the launch of the BRICS Contact Group on Climate Change and Sustainable Development within the framework of the Environment Working Group under the Russian Chairship in BRICS in 2024.
80. The Sides noted with satisfaction the resilience of India-Russia Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership and the convergent and complementary approaches of their foreign policy priorities, and reaffirmed their commitment for its further strengthening. They stressed that India and Russia as major powers will continue to strive for global peace and stability in a multipolar world.
‘
81. Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi thanked President H.E. Mr. Vladimir Putin for the gracious hospitality extended to him and his delegation in Moscow and invited him to visit India in 2025 for the 23rd India-Russia Annual Summit.




 Subscribe Us
Subscribe Us